There are many different routes for the administration of medicines. One method is to insert therapeutic agent via intramuscular route. Intramuscular or IM route is usually given as a shot in the muscles. Individuals who have patients in their home with any chronic illness or those who require medicines through IM route must know the basics of intramuscular administration. The nurse will demonstrate the correct way of administration.
How to Give an Intramuscular Injection
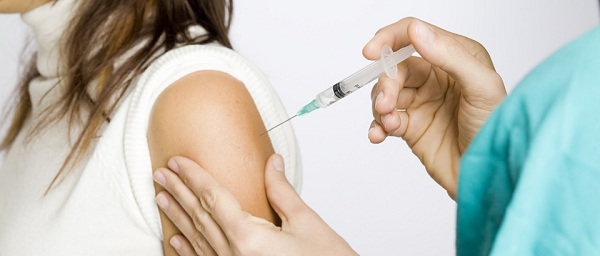
In order to learn how to give IM injection corretly, a person must understand the components of injection first. The following are some major components of injection.
Needle: It is the part which penetrates inside the muscle and releases the therapeutic agent.
Barrel: This holds the active agent. Barrel has a ruler like structure which has markings on it. They correct measurement when pulling out the medicine. Injected medicines are mostly measured in ml (equivalent to cc).
Plunger: It takes the therapeutic agent in and out.
The following are some important steps which must be noticed and followed when injecting any medicine intramuscularly.
Step 1: Clean Your Hands
The hygiene plays an important role. Always wash the hands with a good quality soap and warm water (recommended).
Step 2: Open the Alcohol Wipe
For maintaining the sterility of the localized area, use alcohol wipe. Wipe it over the surface where the needle needs to be inserted. Allow the alcohol to be completely dried off the skin.
Step 3: Prepare the Needle
The needle is covered with a cap so that it will be safe from contaminants and tampering. Remove the cap just like removing a pen cover. Look for any damage over the needle. If tampered, discard the syringe right away.
Step 4: Hold the Syringe
Hold the syringe in the most comfortable position. Make sure that the direction of the needle is downwards. The syringe should be held by the middle finger and thumb with the index finger resting over barrel.
Step 5: Insert the Needle
Place the injection at 90 degree and inject the needle. Make sure that the needle is pushed. When the needle enters, pull it slightly back just to ensure that no blood vessel is ruptured. If blood comes out, take out the needle immediately and discard. Choose another site for injecting the medicine with new syringe.
Step 6: Insert the Medicine
After you correctly insert the needle, start pushing the plunger down slowly. Do not rush while injecting the medication since pushing the medicine too quickly may cause severe pain as well as damage the muscle.
Step 7: Remove the Needle
After injecting the whole medicine, carefully take out the syringe in the same direction as it was entered.
Step 8: Dispose Syringe and Needle
The syringes must not be discarded in the trash bins directly. Syringe and needles should be placed in hard plastic containers. When using a syringe or needle at home, you must ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a plastic container for correct disposition.
Here is a video demonstration of how to give IM injection.
What Are the Correct Places for an Intramuscular Injection?
If you need to administrate IM injection by yourself, finding the correct location is an important part of learning how to give IM injection.
1. 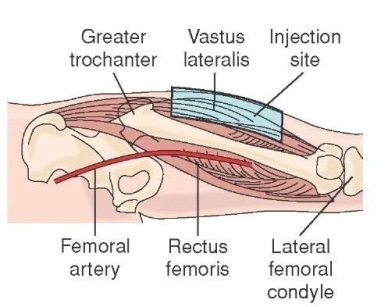 Vastus Lateral Muscle
Vastus Lateral Muscle
These muscles are present on the thigh region. First divide the thigh into three equal segments. The middle region of the divided segments is the part where the intramuscular injection needs to be inserted. This muscle is suggested for children less than three years of age or when self-administration is required.
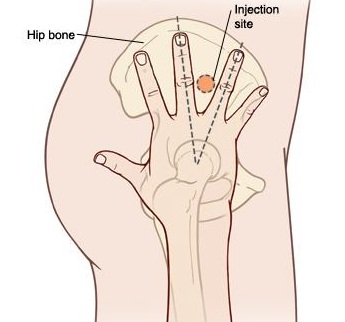 2. Ventrogluteal Muscle (Hip Muscle)
2. Ventrogluteal Muscle (Hip Muscle)
For locating the ventrogluteal muscle, place the heel of one hand on the thigh region where it touches the buttocks, then point the thumb towards the groin and the index finger should be towards his head. Stretch the other fingers so a V will be formed. Insert the Injection in the middle of V (between the middle and the ring finger). This muscle is suggested for children older than seven years of age or for adults.
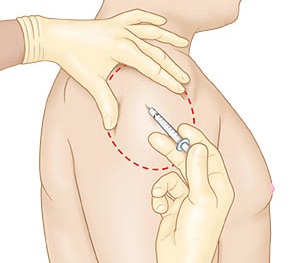 3. Deltoid Muscle
3. Deltoid Muscle
In the upper region of the arm, look for the acromion which is the bone that is present across top of the arm and forms a triangle. Make sure that the triangle should be below the base of the armpit level. After locating the deltoid muscle, carefully inject the medicine in the center of triangle. This muscle should not be selected if the person is having thin upper arm region.
4. Dorsogluteal Muscle
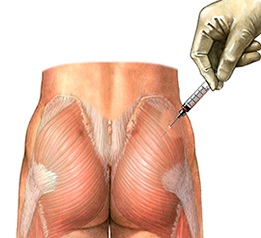 This muscle forms the bulk of your buttocks. Make a line using an alcohol wipe starting from the crack between the buttocks to the side of your body. Look for the middle of the previous line and go up 3 inches. Draw another line from that point across the first line drawn. This should be halfway down to the buttocks (so a cross will be made in this way). The needle needs to be injected in the upper square of the cross drawn. These muscles should be selected when administering an IM injection in children more than three years of age.
This muscle forms the bulk of your buttocks. Make a line using an alcohol wipe starting from the crack between the buttocks to the side of your body. Look for the middle of the previous line and go up 3 inches. Draw another line from that point across the first line drawn. This should be halfway down to the buttocks (so a cross will be made in this way). The needle needs to be injected in the upper square of the cross drawn. These muscles should be selected when administering an IM injection in children more than three years of age.
Note
Different muscles can be selected according to the patient's age and condition. Selecting different sites for every new IM administration will prevent tissue scarring.
How to Select Needle for an Intramuscular Injection
The selection of needle according to the patients’ age, weight and injection site is another component of learning how to give IM injection. The following table can provide you the detailed information.
|
Age |
Weight |
Injection Site |
Length of the Needle |
|
From birth to one month |
Any weight |
Thigh |
16 mm |
|
From one month to one year |
Any weight |
Thigh |
25 mm or 1 inch |
|
From one to two years |
Any weight |
Thigh |
25-31 mm |
|
From one to eighteen years |
Any weight |
Deltoid |
16-25 mm |
|
From two to eighteen years |
Any weight |
Any site (except deltoid) |
25-31 mm |
|
Adult |
Less than 60 kg |
Any site |
16 mm |
|
Adult |
60-70 kg |
Any site |
25 mm |
|
Adult |
Women: 70-90 kg Men: 70-120 kg |
Any site |
25-38.1 mm |
|
Adult |
More than 90 kg |
Any site |
38.1 mm |
When to Seek Medical Care
Contact your healthcare provider:
- When there is persistent fever, coughing or sneezing after the administration
- When you feel lump or bruising on injection site
- If you have swelling which does not go away
Seek immediate medical care if you have:
- Any rash after injection administration
- Breathing problems after injection administration
- Swelling specifically on facial region such as lips and mouth
