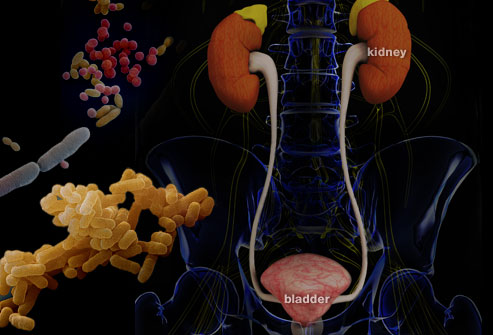
A bladder infection is a urinary tract infection caused by bacteria. This type of infection, like many UTIs, is more common in women than men due to the anatomical differences of their urinary tracts. The shorter urethra in women increases the risk of bacteria traveling up to the bladder. But, although women are more likely to get UTIs, bladder infection in males is not uncommon. And while the symptoms of urinary tract infections are similar in both men and women, some symptoms are unique to men.
What Are the Symptoms of Bladder Infection in Men?
While different individuals will not have the same signs, the following are the most common symptoms of bladder infection:
• A sudden and frequent urge to urinate
• Peeing little amounts of urine
• Lower back pain or cramping in the lower abdomen
• Burning sensation when urinating
• Frequent urination during the night
• Foul-smelling urine that may appear cloudy
• Fever
• Feeling tired
• Blood in the urine – this is a sign that your bladder walls are inflamed, in which case you should seek medical assistance urgently.
The following UTI symptoms are specific to men:
• Discharge from the penis
• Swollen scrotum
It is important to note that bladder infection in males is more likely to recur after the initial infection because bacteria may hide and multiply within the prostate gland.
What Causes Male Bladder Infection?
Bladder infection is normally caused by bacteria which multiply in the urethra and travel into the bladder. These bacteria include Staphylococcus, Escherichia Coli, Klebsiella, and Pseudomonas. If left unchecked, the infection can grow further and reach the kidneys and ultimately, get into the bloodstream.
Although rare, bladder infection in males can sometimes be caused by fungi or other parasites.
Predisposing Factors for Bladder Infection in Men
While bladder infections and UTIs in general are not very common in men, some factors can increase the risk. These include:
- Circumcision – Circumcised men are less likely to develop a bladder infection than their uncircumcised counterparts.
- Age – Due to enlargement of the prostate gland, men who are 50 years and above are more likely to contract bladder infection.
- Pre-existing conditions – Conditions such as kidney stones can cause blockages that would increase the risk of an infection.
- Anal sex – Anal sex increases the risk of getting sexually-transmitted UTIs.
- Disruption in the normal flow of urine caused by a catheter – When the flow of urine is disrupted, it is difficult to wash away the microbes.
- A weak immune system caused by conditions like HIV or diabetes
Note that risk factors only mean that an individual has a higher risk of contracting a bladder infection; it doesn’t mean he will catch it. The opposite applies to those who have a lower risk. They can still get it. For these reasons, it is prudent to always be on the lookout, irrespective of the predisposition or risk factors. It is always better to take measures to prevent an occurrence of an infection.
How Can Male Bladder Infection Be Diagnosed and Treated?
Diagnosis
If you suspect that you have a bladder infection, visit a medical facility where the following tests may be carried out:
- A complete physical examination including reference to any medical history or surgeries
- Rectal examinations to evaluate the state of the prostate
Lab tests such as:
- Urinalysis
- Urine cultures to detect the pathogen causing the infection
- Blood tests
- Intravenous pyelogram (IVP), a series of X-rays that detect any abnormalities in the urinary tract
- Ultrasonography, a test that detects presence of kidney stones
These medical examinations are conducted to identify any underlying problems and conditions that may be the cause of bladder infection in men. The main aim of the medical tests is to rule out any other conditions and identify the causative one. It is worth noting that many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms.
Depending on your situation, further tests may be conducted.
Treatment
The treatment of bladder infections is usually a dose of antibiotics. The dosage depends on the severity of the condition. Typically, a week’s dose of antibiotics will do the job. Your doctor may also prescribe pain and fever medication to manage the symptoms of the bladder infection.
Depending on the severity of the infection, especially if the prostate is infected, treatment may be continued for two to six weeks. It is imperative that you take the full dosage of the medication. Failure to do so will give the bacteria a chance to develop immunity against the particular antibiotic, thus making them stronger.
How to Prevent Recurrence of Bladder Infection in Men
The following lifestyle and diet changes can help prevent recurrence of bladder infection:
- Drinking plenty of water encourages urination which flushes out bacteria from your urinary tract.
- Urinating immediately after having sexual intercourse reduces the risk of infection.
- Keeping a high standard of hygiene, especially before and after sexual intercourse.
- Practice safe sex by using protection and maintaining a single sexual partner.
- Don’t hold in urine for too long; otherwise this will provide an ideal environment for bacteria to multiply.
- If you are a person living with diabetes, always ensure that your blood sugar levels remain under control.
- Make sure that you and your sexual partner are treated for any infections to avoid transmission.
- If you have a weak immune system, maintain a healthy lifestyle that supports your immunity. This includes eating a balanced diet, eating probiotic foods like yogurt, and drinking cranberry juice.
