The ilium is one of 3 bones that form the hip bone. The inside surface of the ilium is a large, concave, smooth surface known as the iliac fossa. Pain of the right iliac fossa (RIF) can be cause for alarm as it is a sign of a number of health conditions such as appendicitis. Like most medical issues, appendicitis presents itself with varied symptoms, and there are several other diagnoses to be considered when a patient is experiencing RIF pain.
Common Causes of Right Iliac Fossa Pain
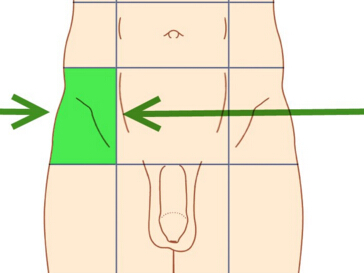
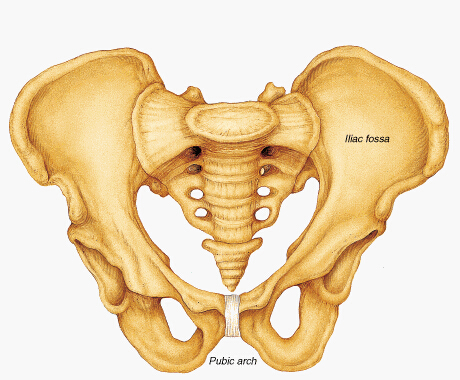
Acute Causes of Right Iliac Fossa Pain
- Appendicitis
The appendix is located on the lower right side of the abdomen. Inflammation of the appendix is called appendicitis and causes pain in that area. At first the pain is usually dull and around the navel, shifting towards the lower right abdomen. As the inflammation becomes more severe, pain increases. Appendicitis can occur to people of any age, even children older than 5 years. Treatment is usually the surgical removal of appendix.
- Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis is the inflammation or infection of the diverticula, which are small pouches that form in your digestive tract. Symptoms of diverticulitis include strong and persistent pain in the abdomen that lasts for several days, nausea, fever, and changes in the bowel movement. The pain is typically on the left side of the lower abdomen, but can also manifest on the right. Mild cases of diverticulitis can be relieved by antibiotics combined with rest, while severe or recurring cases require surgical treatment.
- Urinary tract infection
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection anywhere along the urinary tract from the urethra to your kidneys. Most infections occur in the lower section of the tract, namely the urethra and bladder. UTIs can be present itself as pain around the pelvis and pubic bone, especially in women. This condition is normally treated with antibiotics.
- Ureteric colic
Intermittent and shooting pain can be experienced as a result of ureteric colic. Ureteric colic is most often caused by calculi, or stones, that obstruct the urinary tract.
- In women
A. Pelvic inflammatory disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)is a type of infection in the reproductive system of women. PID symptoms include irregular menstruation, heavy and foul-smelling vaginal discharge, and pain in the pelvic area and lower abdomen. Left untreated, it can lead to chronic painand difficulties getting pregnant.
B. Ectopic pregnancy
When a fertilized egg is implanted outside of the uterus, it is termed an ectopic pregnancy. Ectopic pregnancies can cause pain in the right side of the abdomen, and sometimes in the neck and shoulders. The abdominal pain is often described as cramps. Ectopic pregnancies can also cause vaginal bleeding.This condition is considered a medical emergency, so if you experience any signs or symptoms of it, seek professional help immediately.
- In children: mesenteric adenitis
Inflamed lymph glands in the abdomen are the cause of mesenteric adenitis. Mesenteric adenitis is most commonly found in children 16 years of age or younger. It causes abdominal pain around the naveland in the right iliac fossa.
Chronic Causes of Right Iliac Fossa Pain
- Irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndromeis a common conditioninvolving the large intestine.Symptoms include diarrhea, constipation, bloating, gas, cramps, and abdominal pain. Irritable bowel syndrome needs to be managed on a long-term scale, as it is a chronic condition.
- Crohn’s disease
Crohn’s disease is also known asinflammatory bowel disease. It causes the lining of the digestive tract to become inflamed. Symptoms of Crohn’s disease can be mild or severe, developing gradually over time or acute. The symptoms include diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, malnutrition, and pain in the abdomen.
How to Relieve Right Iliac Fossa Pain
When you experience pain of the right iliac fossa, other than getting diagnosed by a medical professional to allow treatment of the underlying causes, there are also a couple of general things you can try to relieve pain:
Warm Compresses
For women who experience pain in their lower abdomens as a result of reproductive issues or menstrual cramps, warm compresses are quite helpful for relief.
Hydration and Nutrition
Until you are sure of the cause of your abdominal pain, it’s recommended to avoid solid food. Your digestive tract may need to rest if you’re experiencing pain coupled with diarrhea, vomiting, or nausea. Wait for at least 6 hours in between meals. Meanwhile, keep yourself hydrated with fluids such as water, fruit juices or broth.
Note: If you are not sure of the cause of your abdominal pain, aspirin and anti-inflammatory medicines should be avoidedas they can result in bleeding complications that are potentially fatal.
