The bladder, ureters, urethra and kidneys make up the renal or urinary system in humans. Besides excretion, controlling quantity of blood and blood pressure, regulating the amount of metabolites and electrolytes in the body, and stabilizing blood pH are also some of the functions of this system. The amount of urine produced in the human body can vary from 800 to 2000 millilitres depending on the condition of the kidneys and the quantity of liquids consumed. Read on to find out more about the function of urinary system and the diseases that can affect it.
Function of Urinary System
Each part of this system has its own role to play in the maintenance of the body and we are going to look at these functions.
1. Kidney
This pair of organs, placed under the rib cage, works as a filtration 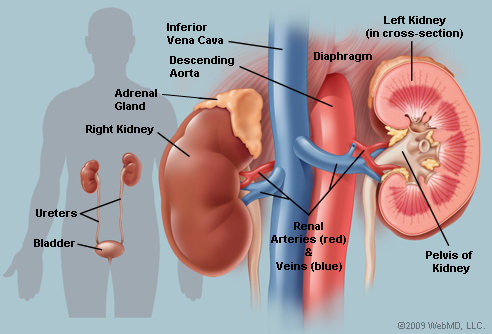 system to remove waste from the blood and form urine. The filtration units called nephrons contain a renal tube and a ball wrapped in small blood capillaries. It also helps maintain the required levels of salts and important nutrients in the blood, and secretes hormones that help generate new red blood cells.
system to remove waste from the blood and form urine. The filtration units called nephrons contain a renal tube and a ball wrapped in small blood capillaries. It also helps maintain the required levels of salts and important nutrients in the blood, and secretes hormones that help generate new red blood cells.
2. Ureter
The ureters are the thin passageways through which urine travels from kidneys to the bladder. The ureter walls are made of muscles that constantly contract and expand to push down the urine formed in the 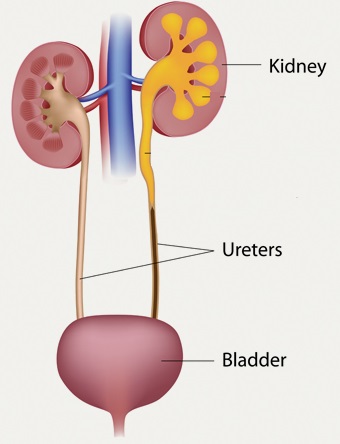 kidneys. A few millilitres of urine are passed through the ureters every 15 seconds. Its blockage can result in a urinary infection, affecting the function of urinary system.
kidneys. A few millilitres of urine are passed through the ureters every 15 seconds. Its blockage can result in a urinary infection, affecting the function of urinary system.
3. Bladder
This works as a reservoir to store urine. It is held in the lower abdomen, by ligaments that connect it to organs and bones in the vicinity. The bladder generally has the ability to hold around 2 cups of urine for a time period ranging from 2 to 5 hours. When a person urinates, the muscular walls of this organ contract to push the urine into the urethra.
4. Urethra
This tube starts from the bladder and allows urine to escape the body. When the bladder’s walls contract, the sphincter muscles relax and urine is pushed through the urethra. Normal function of urinary system needs the brain to send signals to both the bladder muscles and the sphincter muscles in the right order. In males, urine is released through the penis, and in female placental mammals through the vulva.
5. Prostrate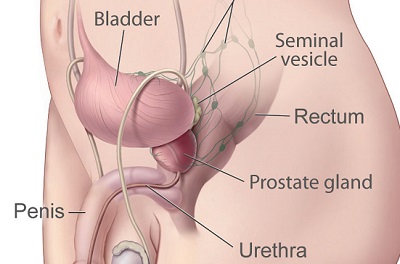
The prostrate is only present in males. It is placed in front of the rectum, between the penis and the bladder. The tube connecting the bladder to the penis runs right through it. The secretions from this gland provide nourishment for sperm. When a male ejaculates, the fluid is secreted into the urethra and combines with sperm to form semen.
6. Others
- Nerves running through the bladder, which signal the brain when the bladder is full.
- Two sphincter muscles surround the exit of the bladder like a rubber band and prevent the leakage of urine from it.
Diseases Affecting Function of Urinary System
Diseases of the urinary system can seriously hamper one's lifestyle, and different specialists focus on diseases affecting different parts. Here are a few of them:
1. Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection, as the name suggests, is an infection caused by bacteria in the urinary tract. The effect of it can spread to other parts like the kidneys, bladder and urethra. It is treated with a course of antibiotics and is more likely to occur in women than in men.
2. Incontinence
This condition results in the leakage of urine from the urinary system. It can be caused by a prolapse in the pelvic region or after a vaginal delivery. Treatment for this condition can be done with physical therapy, pelvic mesh surgery, medicines or vaginal laser surgery.
3. Interstitial Cystitis
This chronic condition is seen mostly in women. The cause for interstitial cystitis has not yet been determined but it can halt the normal function of urinary system by leading to pain in the bladder and pelvis. The bladder may be scarred and less elastic due to this disease. Damage is also seen in the protective covering of the bladder, known as epithelium.
4. Prostatitis
This occurs in the prostate gland; hence this disease is limited to the male urinary system. Advanced age can cause the gland to swell, leading to pressure on the bladder and pain while urinating. Other symptoms are an increase in frequency of urination and pelvic pain.
5. Kidney Stone
These are literally stones formed of calcium oxalate. When chemicals in the urine exceed certain level, they result in the formation of these lumps in the urinary tract. These kidney stones cause pain in the sides and back of the body, and also lead to the presence of blood in urine. It is generally treated with non-invasive methods like extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy which attempts to break the lumps by hitting it with shock waves.
6. Kidney Failure
The kidneys play an important role in the filtering of liquid waste from the body. Its failure can occur temporarily due to diseases like diabetes and hypertension, or as a result of direct trauma. This condition can also become permanent after a complication in the urinary system and the patient will have to undergo regular dialysis.
7. Bladder Cancer
This disease is generally seen in men and elderly people. The American Cancer Society claims that 75,000 Americans are diagnosed with it every year. It results in strong pelvic and back pain, an increase in frequency of urination and trouble urinating normally.
The function of urinary system plays a very important role in maintaining our bodies and a disease in any body part requires immediate medical attention. Nephrologists, urologists and gynaecologists are some of the specialists who can treat these diseases.
