Gestational diabetes refers to a condition in pregnant women in which the body fails to produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar. In most cases, it is a temporary condition and becomes normal after delivery. Also called carbohydrate intolerance or glucose intolerance, gestational diabetes is more common in pregnant women who are obese and are over the age of 35. You are more likely to develop this condition during pregnancy if you have a family history of diabetes. While your doctor will ask for a testat some point during your pregnancy, it is good idea to go for regular testing to avoid dealing with any complications later.
Why Is It Important to Have Gestational Diabetes Test?
Statistics show that about 2-5% of all pregnant women end up developing gestational diabetes. If you have risk factors, you are more likely to develop it. Your doctor usually orders tests for gestational diabetes betweenyour 24th and 28th week of pregnancy because this is usually the time when your placenta produces large amounts of hormones, which may lead to insulin resistance.
Having gestational diabetes test is significant because, left untreated, it can have negative impact on you and your baby. You baby may grow too big due to the extra glucose, causing difficulty when giving birth or even pre-term birth. Besides, your baby may also experience jaundice, low mineral and blood sugar levels and temporary breathing problems. And you yourself may have greater risk of preeclampsia or type 2 diabetes after delivery.
What Gestational Diabetes Test Will You Have?
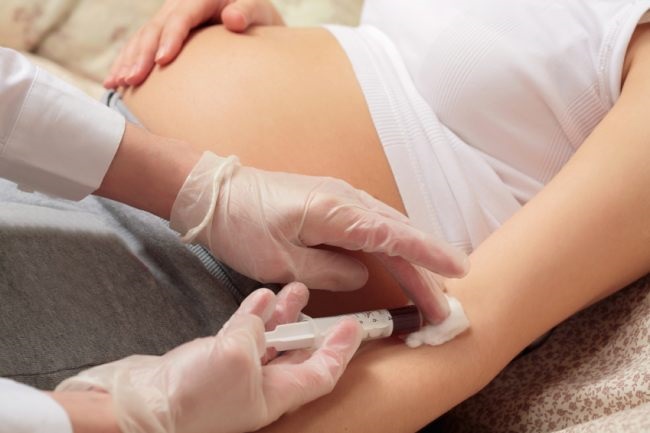 It is important to keep an eye on your blood glucose level during your pregnancy. This helps identify issues early to prevent further complications. Routine screening will help find out if you have gestational diabetes or not. This may involve the following:
It is important to keep an eye on your blood glucose level during your pregnancy. This helps identify issues early to prevent further complications. Routine screening will help find out if you have gestational diabetes or not. This may involve the following:
1. Initial Glucose Challenge Test
You will have a blood test after an hour of drinking a syrupy glucose solution. Your test results are normal if your blood sugar level is below 130mg/dL – this may vary a bit from lab to lab. With test results higher than normal, you will have to go for a glucose tolerance test to confirm if you really have gestational diabetes.
2. Glucose Tolerance Testing
You need to avoid eating anything overnight and come for the test in the morning for accurate results. Your doctor will then make you drink a glucose solution and check your blood sugar again after an hour for three hours. You have gestational diabetes if at least two of the blood sugar readings are higher than normal.
3. If Diagnosed with Gestational Diabetes
After your gestational diabetes test confirms that you have this condition, your doctor will ask you to come for regular checkups, especially during your last trimester. They may prescribe medications to help keep your blood sugar level in check. In some cases, you need to take insulin to control your blood sugar. Other tests may also be ordered in case you develop other pregnancy complications as well. These tests may help assess the function of the organ that delivers nutrients and oxygen to your baby. It is equally important to monitor your baby's well-being when your gestational diabetes is not completely under control.
4. Blood Sugar Testing after Delivery
It is important to have your blood sugar monitored for at least 6-12 months after your delivery. In most cases, your tests become normal after delivery, but even then, you need to have your diabetes risk assessed at least once every three years. It is not uncommon to have your future tests show blood sugar levels higher than normal but not high enough to be called diabetes. Talk to your doctor and they will explain how to make some lifestyle changes to avoid developing diabetes.
How to Treat Gestational Diabetes
If your gestational diabetes test is positive, it is important to follow a treatment plan to keep blood sugar under control.
1.  Eat Balanced Meals
Eat Balanced Meals
You need to stick to a healthy diet – work with a dietician to create a perfect eating plan. It is important to limit your intake of carbs. It also helps to keep a record of what you eat. Keep track of your body weight and take steps to keep it within normal range.
2. Stay Active
 You need to exercise at least 2½ hours every week. It needs to be moderate exercise. The best thing is to engage in moderate exercise for 30 minutes five days a week. Moderate exercise helps regulate insulin, which in turn helps control your blood glucose level. Low-impact activities such as swimming or walking work great, but it is a good idea to talk to your doctor and ask about exercises you can perform safely.
You need to exercise at least 2½ hours every week. It needs to be moderate exercise. The best thing is to engage in moderate exercise for 30 minutes five days a week. Moderate exercise helps regulate insulin, which in turn helps control your blood glucose level. Low-impact activities such as swimming or walking work great, but it is a good idea to talk to your doctor and ask about exercises you can perform safely.
3. Check Blood Sugar Levels Regularly
 Even when you are taking steps to control blood sugar, you should never overlook the importance of checking your blood sugar regularly. It is of immense importance to keep your blood sugar levels within a target range, and that is possible only when you check your blood sugar regularly. Your doctor will guide you about how often you need to test your blood sugar.
Even when you are taking steps to control blood sugar, you should never overlook the importance of checking your blood sugar regularly. It is of immense importance to keep your blood sugar levels within a target range, and that is possible only when you check your blood sugar regularly. Your doctor will guide you about how often you need to test your blood sugar.
4. Monitor the Growth of Your Baby
Just like paying attention to your own health, it is equally important to monitor fetal growth when you have developed gestational diabetes. You will have to keep tract of "kick counts" or fetal movements to ensure your baby is growing normally. Talk to your doctor immediately if you notice less than usual fetal movement. Fetal ultrasounds also helps confirm if the baby is growing in a healthy way or not.
5. Take Your Medications as Prescribed
 It is possible to keep your gestational diabetes in control by making lifestyle changes and sticking to an exercise plan, but sometimes you need more than just that. Your doctor may prescribe medications and give you insulin injections to control your blood sugar. About 10-20% of women with this condition require insulin shots. Sometimes, your doctor may prescribe oral medications to control blood sugar. Talk to them about how often to take those medications.
It is possible to keep your gestational diabetes in control by making lifestyle changes and sticking to an exercise plan, but sometimes you need more than just that. Your doctor may prescribe medications and give you insulin injections to control your blood sugar. About 10-20% of women with this condition require insulin shots. Sometimes, your doctor may prescribe oral medications to control blood sugar. Talk to them about how often to take those medications.
