The function of the retina can affect people's peripheral vision. Blurred peripheral vision can be caused by conditions which are not serious such as asthenopia, but serious conditions could also be culprits. It is advisable for you to visit your doctor whenever you experience blurry vision to avoid further complications such as loss of vision.
Causes and Treatment for Blurry Peripheral Vision
1. Migraine

Migraines are severe headaches caused by narrowing of the blood vessels (vasoconstriction), followed by widening of the vessels (vasodilation). When the vessels are narrowed, blood flow is reduced, which affects the eye. This can lead to peripheral blur or central blurred vision.
Treatment
- Abortive or acute treatment. This involves taking pain relief drugs when you have migraine attacks.
- Preventive medications. Taking these medications on a daily basis can help relieve the pain and reduce the frequency of migraines.
Non-traditional therapies like massage therapy and acupuncture may also help in this situation.
2. Giant Cell Arteritis

This is an inflammation that affects the lining of the arteries. It usually affects arteries in the head, especially the ones in your temples. Giant cell arteritis causes scalp tenderness, headaches, vision problems such as blurry peripheral vision, and jaw pain. Below are some other symptoms you may experience:
- Fever
- A chronic headache in the temple area
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
Treatment
Treatment for this condition involves taking high doses of corticosteroid drugs like prednisone. You may have to take these medications for a long time, usually one or more years. The dosage will be reduced gradually after the first month until the best possible result is achieved.
3. Optic Disc Drusen
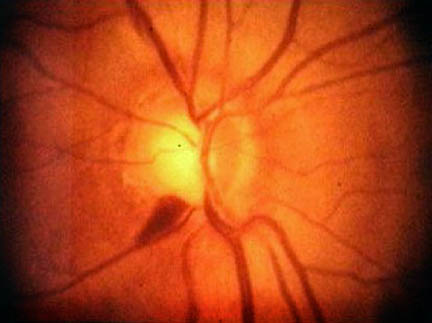
Drusen are deposits under the retina, the light-sensitive tissue in the eye. They are usually yellow in color and comprise of a fatty protein called lipids. Usually, optic nerve drusen (hard drusen) don’t have symptoms. However, some people with this condition may experience vision problems such as temporary flickering or loss of peripheral vision.
Treatment
Hard drusen don’t really need any treatment. If hard drusen are detected by your ophthalmologist during a routine eye exam, he/she may suggest you pay closely attention to them in case they develop into soft drusen which are more serious.
4. Papilledema

Papilledema is an eye condition caused by increased pressure around or in the brain. It can make part of the optic nerve in the eyes swell. Symptoms of this eye condition include:
- Blurry peripheral vision and decrease in color perception may occur.
- Transient vision obstructions may also be experienced by some patients.
Treatment
- If a brain tumor is responsible for the increased pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid, drugs such as corticosteroids may be prescribed. Surgery may also be carried out to remove or reduce the size of the tumor.
- If papilledema occurs due to idiopathic intracranial hypertension, it can be treated with diuretics and weight loss. If this treatment won't work, surgery may be done.
- If it is caused by bacterial infection, antibiotics will do the job.
5. Asthenopia

Asthenopia refers to certain different symptoms that lead to red eyes, pain around or in the eyes, eye strain and fatigue, rare double vision, blurred peripheral vision, and severe or mild headache. These are usually felt after using the computer for a longer period.
Treatment
The best way to relieve this problem is to spend less time in front of the computer and to adjust your work stations properly. Putting on glasses can help to reduce eyestrain.
6. Glaucoma
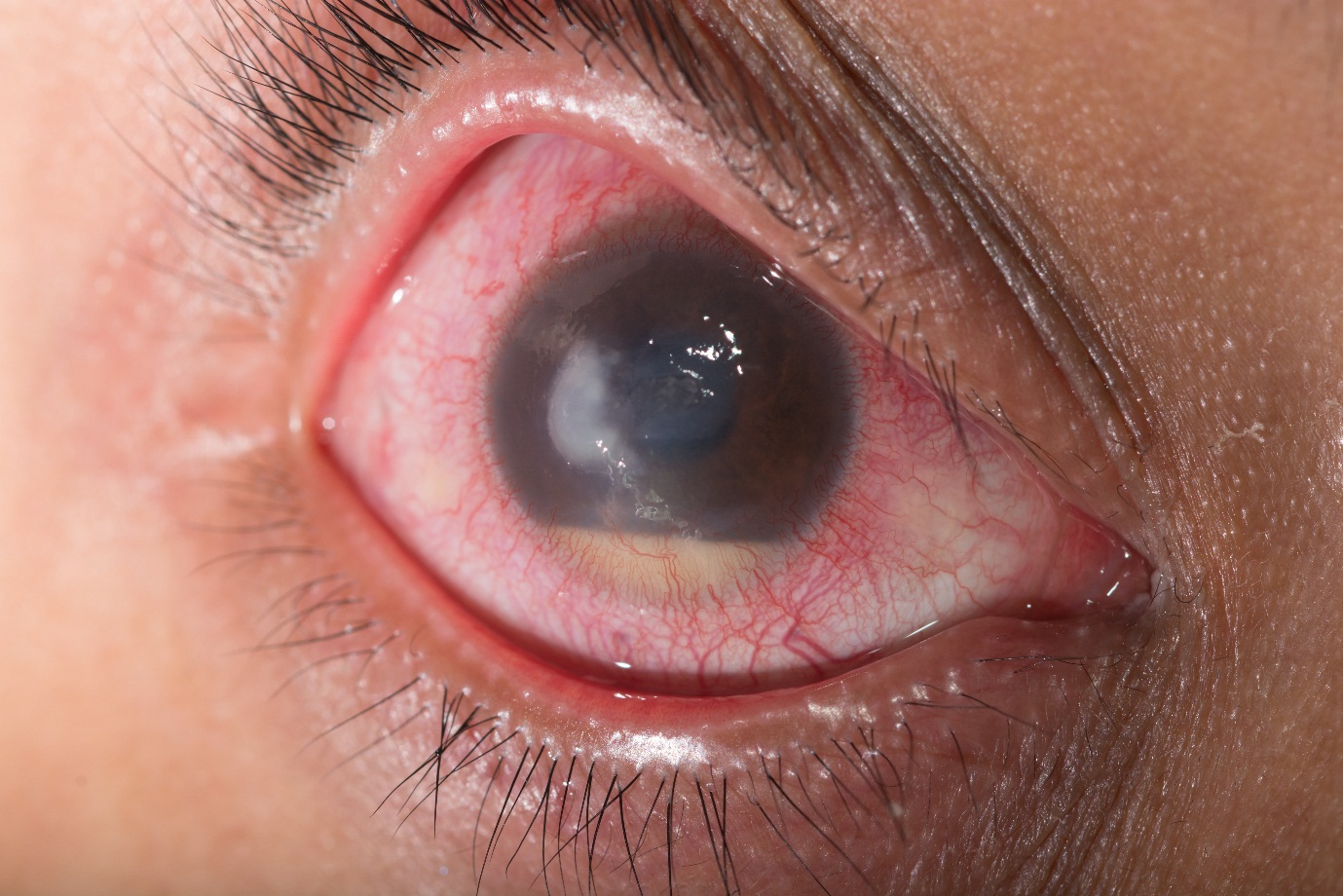
Glaucoma is a combination of eye conditions that cause damage to the optic nerve, a nerve that aids good vision. This condition is usually caused by abnormally high pressure in the eye. Symptoms and signs may vary a lot, depending on the stage and type of the condition. For acute angle-closure glaucoma, the symptoms may involve eye pain, blurry peripheral vision, nausea and vomiting.
Treatment
The main objective of treating glaucoma to lower the intraocular pressure in the eye. Depending on the severity, eye-drops such as beta-blockers and alpha adrenergic agonists, prostaglandins, and laser treatment may be given. In serious cases, surgery is an option.
7. Corneal Edema
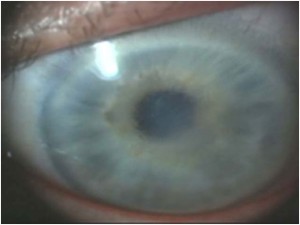
Corneal edema happens when the cornea swells. The cornea is a thin and transparent layer that covers the iris of the eye. Cornea is responsible for a clear and crisp vision. In healthy people, the cornea is lubricated with new tears, and then the old one is drained out to maintain that the cornea's shape consistent and even. People who suffer from corneal edema have a swollen and distorted cornea which causes blurred vision.
Treatment
If you are using contacts, the doctor will suggest you avoid using them for some time. The treatment often includes flushing out the excess fluid that accumulates in the cornea. Pain medications will also be prescribed to relieve discomfort. If this treatment does not work, surgery may be the last option.
