A lung biopsy is kind of medical procedure in which growths or tissues are removed from the lungs and examined under a microscope. It is done to help diagnose cancer of the lung or other lung disease. A lung biopsy is generally recommended after an abnormality is detected in a chest X-ray or CT scan. There are two types of methods used to perform a lung biopsy: open and closed. Closed methods are done via the trachea (windpipe) or the skin and open methods are done in the operation theatre under general anesthesia.
Lung Biopsy Procedure
How to Do the Preparation for Lung Biopsy?
Discuss with your physician regarding any concerns you may have about the biopsy, its risks, its procedure and what will be the significance of results.
Before you undergo the procedure, tell your physician if you:
- Are on any medications.
- Have allergy to any drugs, including drugs used in anesthesia.
- Have any problems related to bleeding or are on blood thinning drugs such as warfarin, plavix or aspirin.
- Are or may be pregnant.
The physician may recommend some blood tests including clotting factors and a CBC (complete blood count) before the procedure.
Your physician will advise when to stop drinking and eating before biopsy. You should follow these instructions about drinking and eating exactly. If you have been instructed to consume your medications by your physician on the day the surgery has to take place, do so by drinking only one sip of water.
A bronchoscopic or needle biopsy does not require hospital stay whereas an open biopsy needs you to stay in the hospital for a couple of days.If you are not required to stay at the hospital after the lung biopsy procedure, have someone to drive you back home.
How Is the Biopsy Performed?
You will be required to remove contact lenses or eyeglasses, dentures, a wig, hearing aids, jewelry and makeup before the procedure. You will be asked to urinate before the procedure. You will be asked to remove most or all of your clothing during the procedure (you may keep on wearing your undergarments if they do not cause interference with the procedure). You may be given a paper covering or cloth during the procedure.
- Bronchoscopic Biopsy
It is performed by a pulmonologist (a physician who is specialized in problems of lungs). It is done by using a flexible and thin bronchoscope. Rarely, a rigid bronchoscope may be used to perform a biopsy.
It generally takes between ½ an hour and 1 hour to do bronchoscopy. You have to remain in recovery room for one to two hours. A CXR is generally done after lung biopsy to find out any problems due to the procedure.
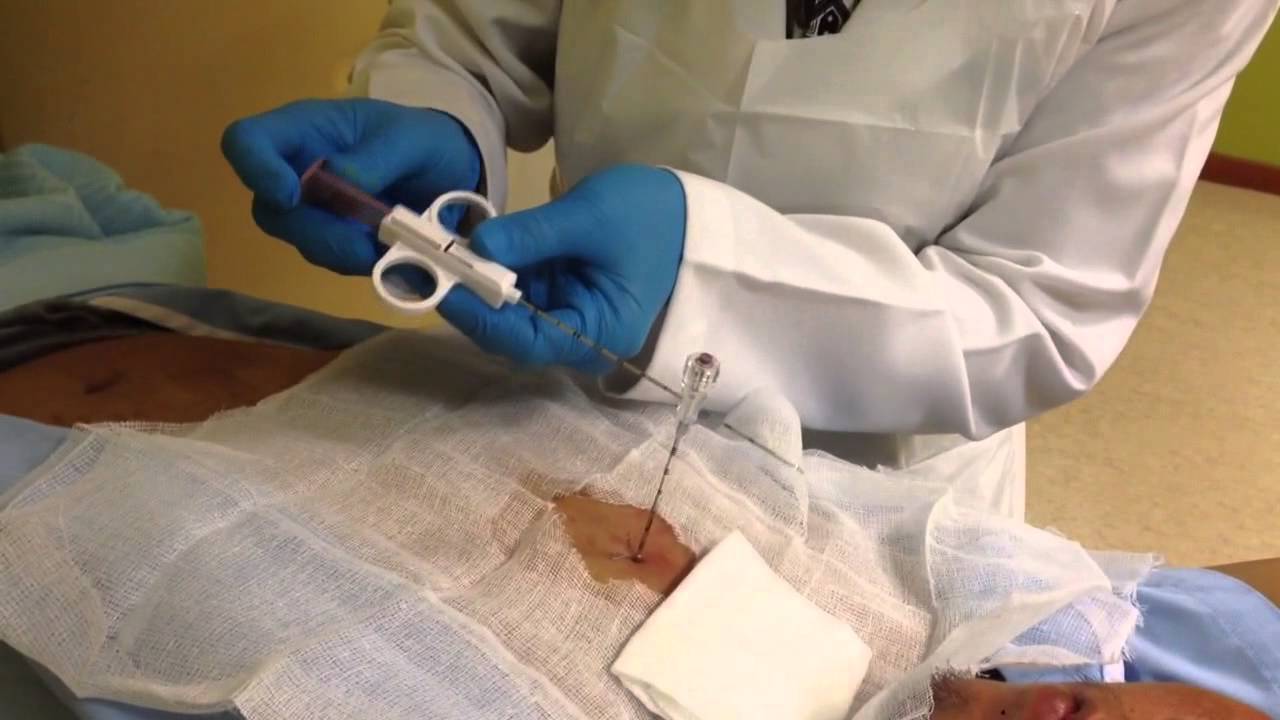
- Needle Biopsy
It is performed by either a pulmonologist or a radiologist. The physician will use an ultrasound, fluoroscopy or CT scan for guiding the needle used for biopsy. The area where the needle is put in your chest is cleaned with antiseptic and draped using sterile towels. Local anesthesia will be given in the area where needle is put in the chest to prevent feeling of pain.
A tiny puncture will be made and you will be asked to hold your breath when the needle is inserted by your physician into the lung. It is imperative to avoid moving or coughing when the needle is placed in the lungs.
Once the required quantity of tissue from the lungs is collected, biopsy needle is taken out. After that a bandage is applied on the site of puncture. You will be required to lie on the side where biopsy is done for about one hour so that the puncture site is sealed.
The biopsy takes around ½ an hour to 1 hour. You have to remain in recovery room for one to two hours. A CXR is generally done after lung biopsy procedure to find out any problems due to the procedure.
- VATS (Open Biopsy and Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery)
An open biopsy is performed by a general surgeon or thoracic surgeon. General anesthesia is required for this procedure.
A sedative may be given to you an hour before the procedure to help you relax. An IV line is placed in one of your veins. A breathing tube is put in your trachea and you may be helped by a machine for breathing.
A cut is made on the area over the lungs from where the sample has to be removed. A thoracoscope is inserted through the incision to visualize the lung surface and to collect the tissue sample.
Once the sample is removed, a chest tube/drainage tube is inserted and the incision is closed by applying stitches. One end of this drainage tube remains in the area surrounding your lungs and other end is outside connected to a container. The aim of the drainage tube is to help your lung re-expand. They are removed from the chest in a couple of days. The stitches are usually removed after 8 to 14 days.
The whole procedure takes around 1 hour. You will be required to stay in recovery room for another hour. You are then transferred to the hospital room.
A CXR is generally done after the procedure to detect any problems due to lung biopsy procedure.
Recovery After the Procedure
The time required to recover after a lung biopsy depends on multiple factors including the kind of procedure done.
A stay in hospital may be needed if the procedure is done under general anesthesia. If the procedure has been done under local anesthesia, then the patient may be discharged as soon as their pulse and blood pressure stabilizes.
In certain cases, scans may be done after lung biopsy. These are done to detect any problems due to the procedure.For instance, lung collapse is a complication that may develop after needle biopsy. A CXR is done a couple of hours later to detect any leakage of air.
It is recommended that you rest for several days after the procedure. You should avoid physical exertion unless advised as safe by a medical professional. Follow-up appointments with your physicians are required to discuss the results of the procedure.
After lung biopsy procedure, call your physician immediately if you develop:
- Severe pain in chest
- Trouble in breathing
- Feeling of lightheadedness
- Excessive bleeding from the site of biopsy
- Coughing up blood (greater than a tbsp)
- Fever
Results
Results from lung biopsy are available in 3-4 days. However, it may require few weeks before you get the results for biopsy samples.
Results: Normal
Lung tissue appears normal under microscope. There are no signs of inflammation, infection or cancer.
Results: Abnormal
Abnormal tissues or cells may be present due to certain diseases of the lungs, active infection, or cancer. If cancer is detected, biopsy results can help determine the treatment options (radiation, surgery or chemotherapy).
